UNIT 2: Optics
Electromagnetic wave
nature of light
Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. This means that
light is a wave that is made up of electric and magnetic fields.
These fields are perpendicular to each other and to the
direction of the wave's propagation
1. State law of
reflection and Snell’s law of refraction
with diagram.
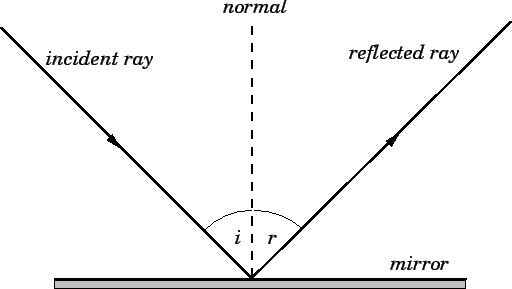
law of reflection:
the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface of the
mirror all lie in the same plane.
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
Snell’s law:
1. The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal at the point of
intersection, all lie in the same plane.
2. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence (i) to the sine of the angle
of refraction (r) is equal to the refractive index of the medium, which is a
constant.
sin i/sin r = μ
2. What is
unpolarised light and plane polarised light?
Unpolarized light: Light
in which vibrations of electric field are in all possible directions, which are
perpendicular to the direction of propagation.

Polarized light : the
light in which vibrations of electric field vectors are confined to one plane,
and other vibrations are blocked.
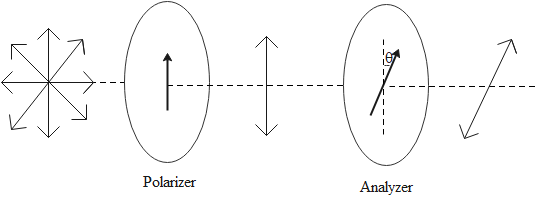
3. State law of
Malus.
When a polarized light passes through another polarizer (analyser),
making angle theta (θ) with the first polarizer, then the intensity of light
becomes I = I0 cos2θ
**[ For any numerical related, write the above formula
To get at least 1 mark]**
4. Explain refraction
of light from denser to rarer medium. Hence explain total internal reflection.
Refraction: The
phenomena of bending of a light ray when it travels from optically rarer medium
optically denser medium , or vise-versa, is called refraction of light.
When a ray of light passedfrom a denser medium to a rare
medium it bends away from the normal in the a rare medium.
Snell’s law for this case may be written as
sin θ2 = (μ1/μ2) sin θ1
Where θ1 is the angle of incidence of light ray in the
denser medium and θ2 is the angle of
refraction in the rarer medium. Also μ1> μ2
• If θ1< θc, the ray refracts into the rarer medium.
• If θ1= θc, the light grazes the interface of rarer to
denser medium
• If θ1> θc ,the ray is reflected back to the denser
medium.
The phenomenon in which light is totally internally
reflected from a denser to rarer medium boundary is called total internal
reflection.
5. Define
(i) Plane of vibration: The plane in which vibration of polarised
light takes place is called plane of vibration.
(ii) plane of polarisation: The perpendicular plane to the plane of vibration in which
there are no vibration is called plane of polarisation.


Comments
Post a Comment